What is UV400 ?
UV400 is UVA. UVA range is 315 – 400nm
400 is the maximum of UVA and also the most dangerous UV.
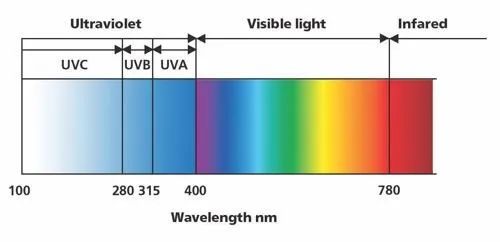
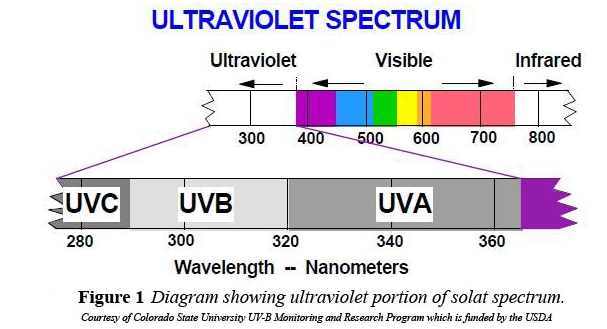
Ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that has a wavelength between 100nm and 400nm. It is part of the sun’s light spectrum that reaches the earth. UV radiation breaks down into wavelengths that are invisible to the naked eye.
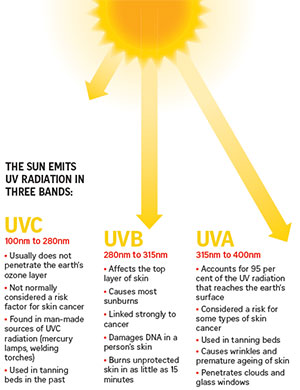
THE SUN EMITS UV RADIATION IN THREE BANDS:
UVC 100nm to 280nm
Usually does not penetrate the earth’s ozone layer not normally considered a risk factor for skin cancer found in man-made sources of UVC radiation (mercury lamps, welding torches) used in tanning beds in the past
UVB 280nm to 315nm
Affects the top layer of skin causes most sunburns linked strongly to cancer damages DNA in a person’s skin burns unprotected skin in as little as 15 minutes
UVA 315nm to 400nm
Accounts for 95 per cent of the UV radiation that reaches the earth’s surface considered a risk for some types of skin cancer used in tanning beds causes wrinkles and premature ageing of skin penetrates clouds and glass windows
UV Class
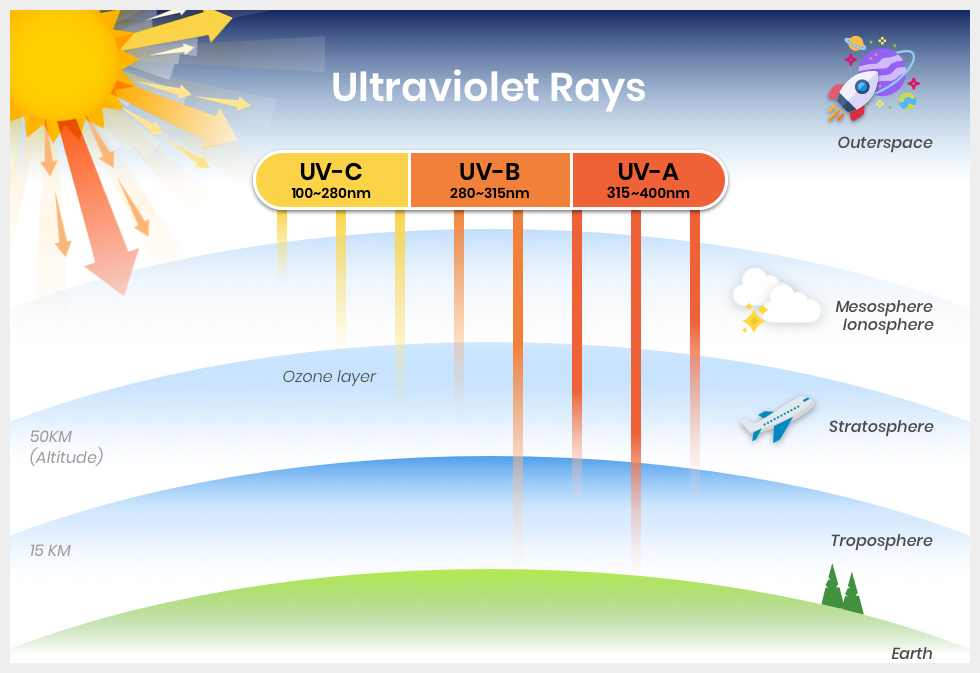
UV radiation levels vary substantially with time and place. The increased risk of UV damage to the skin and eye during a holiday in a sunny location is often underestimated. Ozone depletion, as well as seasonal and weather variations, cause different amounts of UV radiation to reach the Earth at any given time. An easy way to tell how much UV exposure you are getting is to look for your shadow: If your shadow is taller than you are (in the early morning and late afternoon), your UV exposure is likely to be lower. If your shadow is shorter than you are (around midday), you are being exposed to higher levels of UV radiation. Seek shade and protect your skin and eyes.
While some exposure to sunlight can be enjoyable, too much can be dangerous. Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can result in a painful sunburn. It can also lead to more serious health problems, including skin cancer, premature aging of the skin, cataracts and other eye damage, and immune system suppression. Children are particularly at risk.
How Does Ultraviolet Light Affect Humans?
DNA Damage
Ultraviolet light is sometimes referred to as ultraviolet radiation. It comes from wavelengths of light that are produced by the sun and other light sources but which are invisible to the human eye. This wavelength of light is able to penetrate into cells and cause damage to their DNA. The high energy light rays of UV light are able to cause chemical changes within the DNA molecules, changing their chemical structure and breaking bonds. As MedlinePlus explains, this can cause the skin cells to become weak and die off, leading to the skin appearing to be abnormally old. This skin damage can also cause wrinkles to occur. In some cases the DNA damage causes genetic mutations, which can lead to skin cells growing unusually quickly. When this happens, it can lead to skin cancer; high amounts of UV exposure is a leading risk factor for the development of skin cancer.
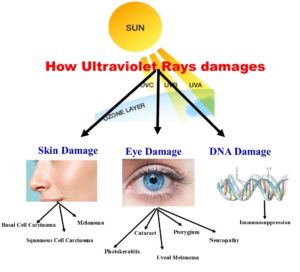
Eye Damage
NASA explains that ultraviolet light can also cause vision problems by damaging the eye. Ultraviolet light can cause damage to the cornea, which makes it cloudy. Sometimes this form of blindness is called “snow blindness” because it can be caused by ultraviolet light reflecting off of snow on the ground. Chronic exposure of the cornea to UV light can also increase the risk of developing cataracts, particularly for people who live at high altitudes or near the equator (where the sun rays are the most intense). UV light damages the cornea similarly to how it damages skin cells–by causing DNA damage that injures or kills the cells of the cornea.



